Fire protection
Steel sheet piles are a versatile and cost-effective solution for use as permanent retaining walls in underground car parks, tunnels, and other underground constructions. Their main functions include retaining soils and water during the temporary excavation phase and the permanent phase, as well as forming permanent exterior structural walls that can transmit high vertical loads from floors or from superstructures to the soil.
Underground car parks | Fire resistance
This brochure provides assistance in the fire safety design of steel sheet piles used as permanent retaining walls in underground car parks or roadworks (tunnels, underpasses, ...).
Fire Safety and Resistance
Steel sheet piles used in permanent underground structures are often overlooked due to misconceptions regarding their ability to withstand high temperatures in case of a fire. ArcelorMittal conducted extensive fire tests and numerical simulations to demonstrate that steel sheet pile walls can achieve significant fire resistance with the appropriate design and additional protection measures in case of need.
Fire Protection Strategies
Fire resistance for steel sheet piles can be achieved through a combination of active and passive protection measures
- Active measures: include systems such as fire and smoke detectors with an automatic sprinkler system that quickly detect and limit the spread of fire.
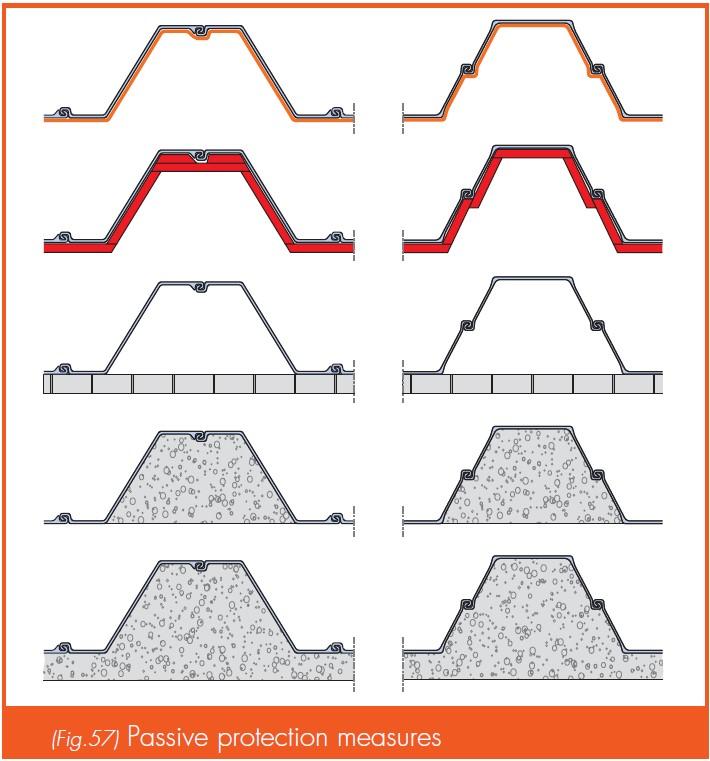
- Passive measures: aim to prevent excessive temperature buildup in load-bearing structures. This can be achieved using:
- Protective coatings: application of intumescent paints or sprays that expand in response to heat to provide an insulating layer.
- Insulating panels: attach panels to provide thermal insulation.
- Masonry: add brickwork or stone in front of the steel sheet pile wall to act as a thermal barrier.
- Concrete fill: fill the inner pans of the sheet piles with concrete to enhance heat transfer resistance.
- Complete concreting: cover completely the face of the sheet piles in concrete for higher fire protection.
Testing and simulation of fire behavior
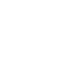
The fire resistance characteristics of steel sheet piles have been extensively tested in a laboratory at the University of Liège, Belgium. These tests involved using different soil types and with different water contents to evaluate thermal conductivity and the impact of the soil on the behaviour of the steel sheet piles under high temperatures. Key outcomes of these studies include:
Thermal conductivity of soils
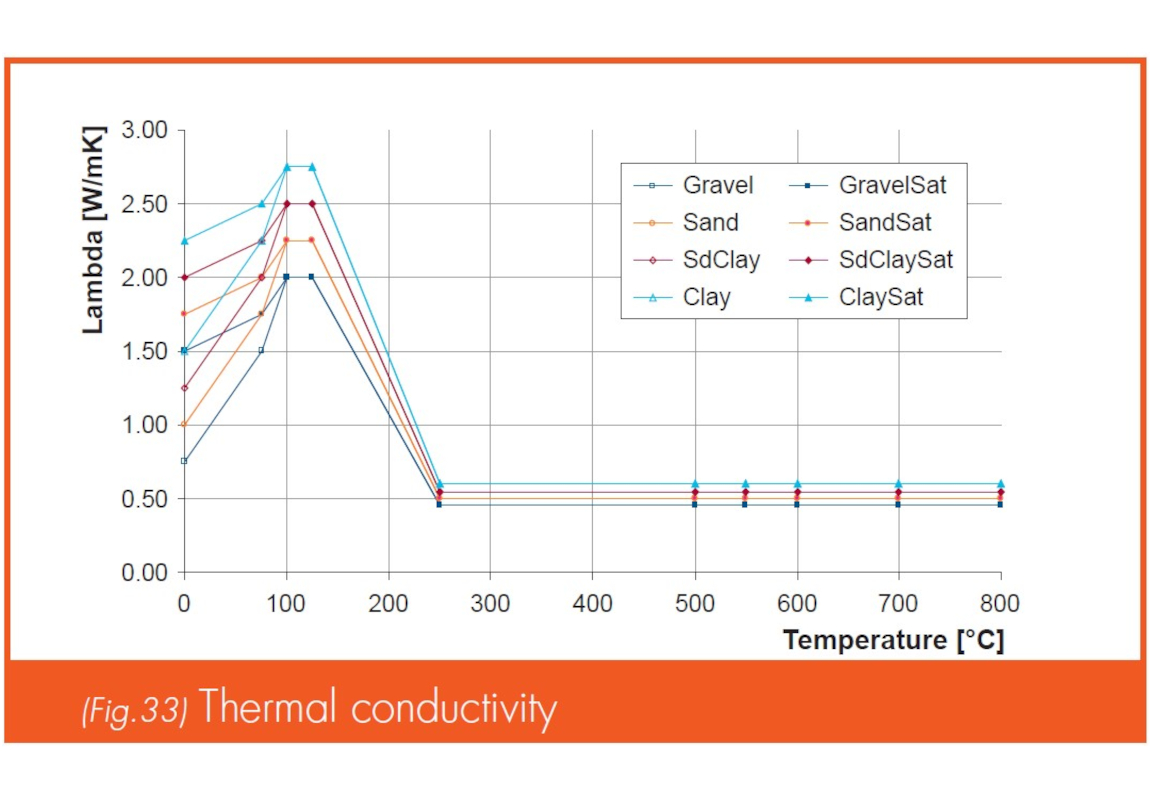 Soils with different characteristics and soil moisture have a different thermal conductivity. Extensive FE-simulations (back-calculation of tests) allowed to calibrate the thermal properties of a two typical soils with different saturation levels.
Soils with different characteristics and soil moisture have a different thermal conductivity. Extensive FE-simulations (back-calculation of tests) allowed to calibrate the thermal properties of a two typical soils with different saturation levels.
Fire testing with soils
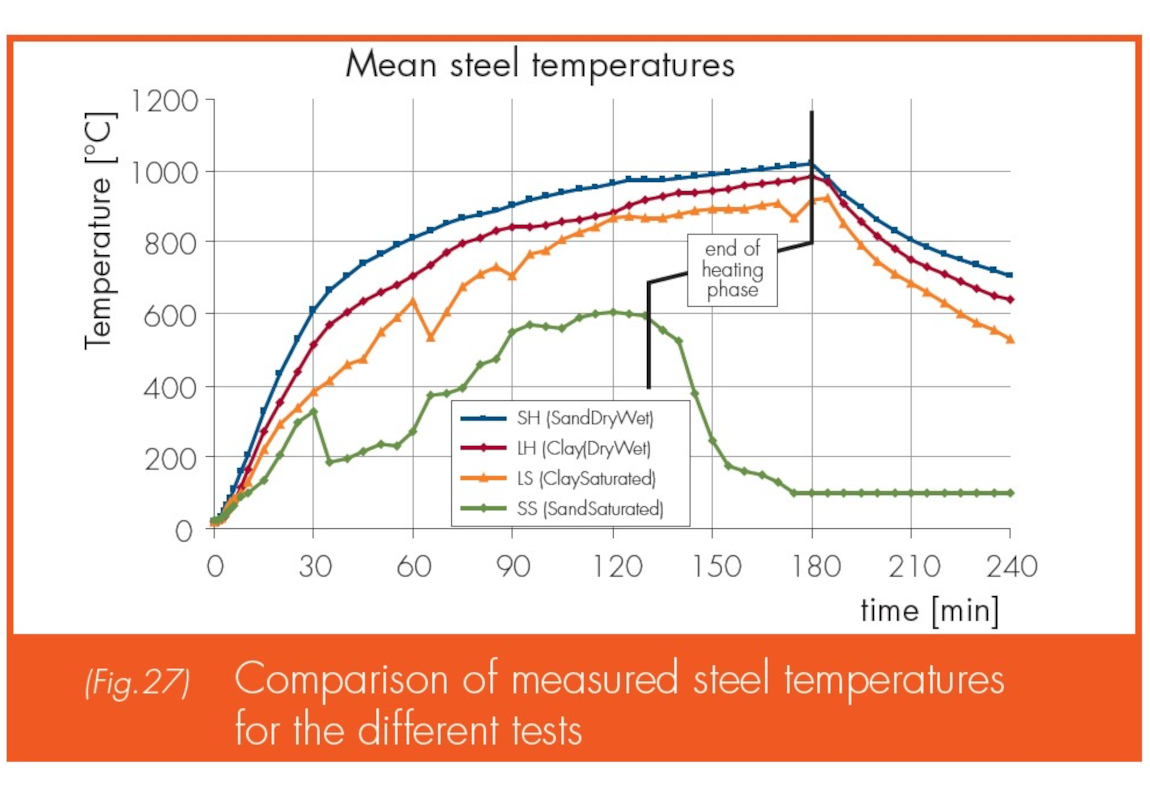
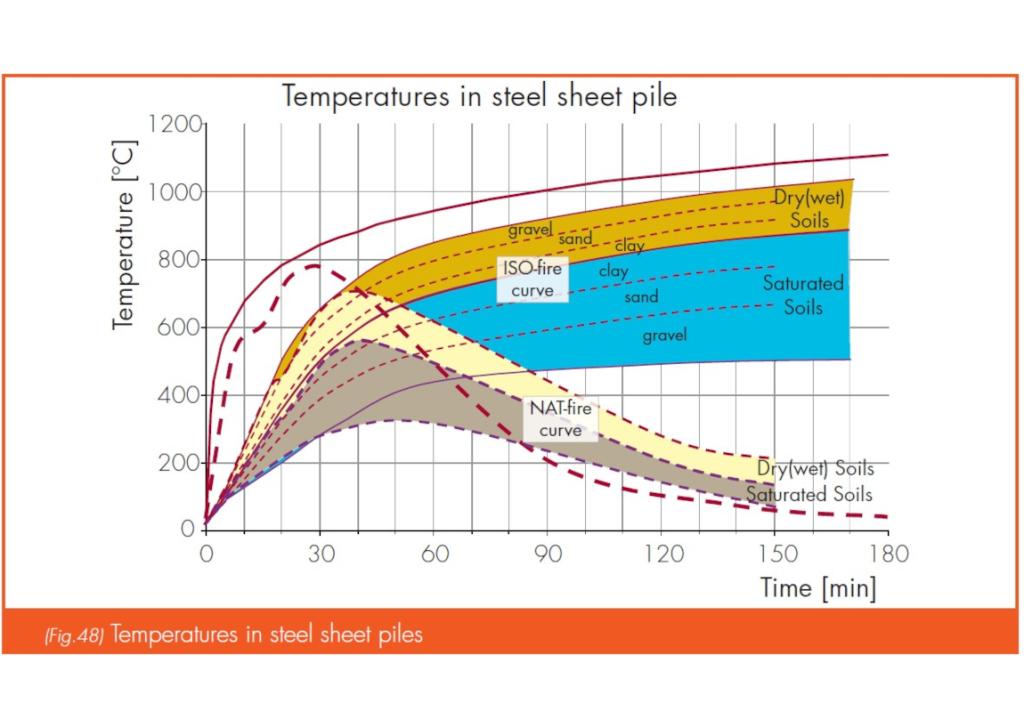
Tests conducted with different types of soils (clay, sand) at various moisture levels showed that saturated soils reduce the heating rate of steel, enhancing fire resistance.
Fire testing setup
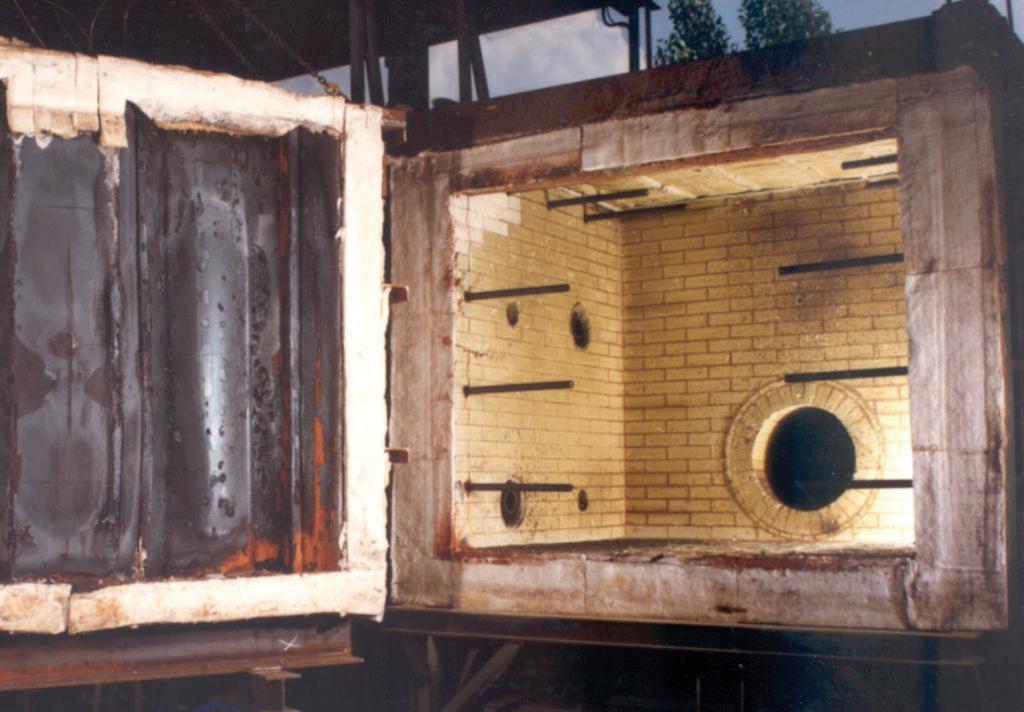

Tests were performed using a specially designed test furnace, with steel sheet piles retaining different soils. The temperatures of the sheet piles and in the soils were monitored at different locations both in the heating and cooling phases of the fire simulation.
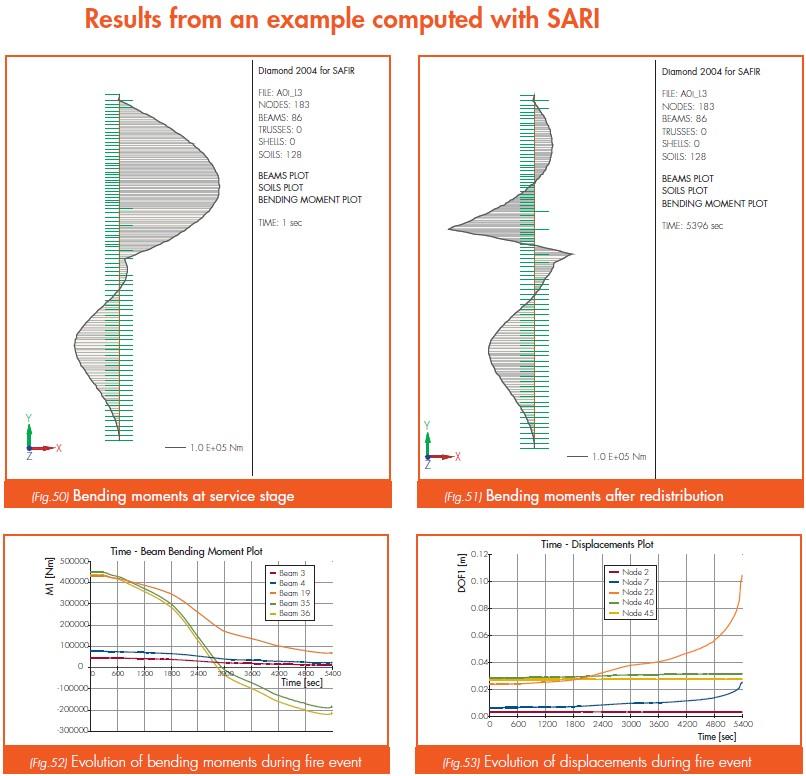
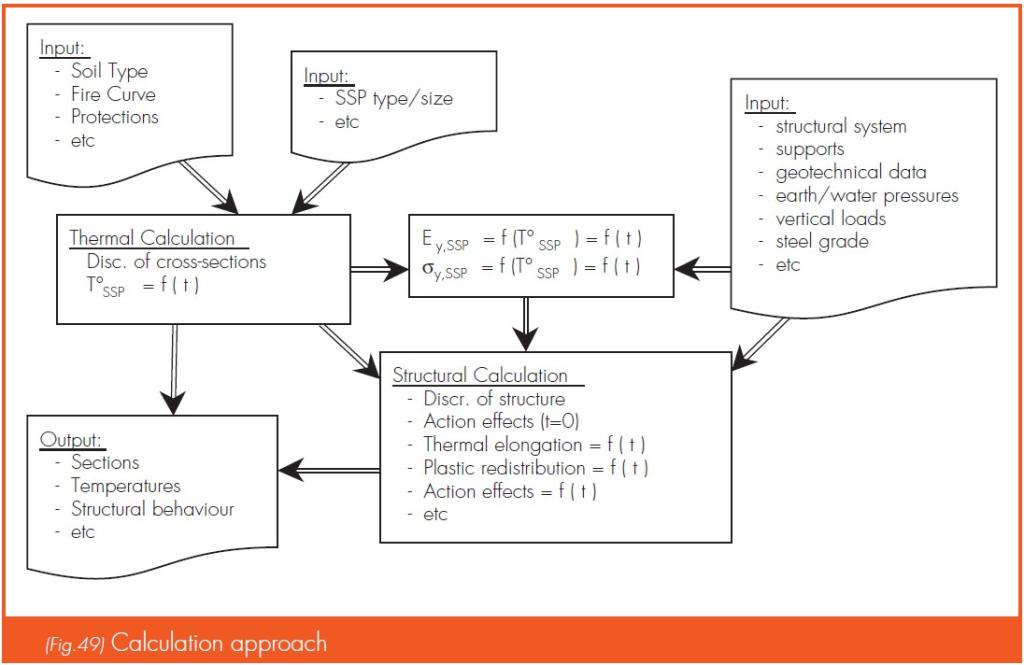
Computing structural behaviour during fire events
ArcelorMittal's engineers can provide assistance in verifying the fire resistance of any steel sheet pile structure under fire. They use advanced software such as SARI (developed by the University of Liège, Belgium) to simulate fire conditions and evaluate structural safety. The software allows detailed thermal and structural analysis, considering
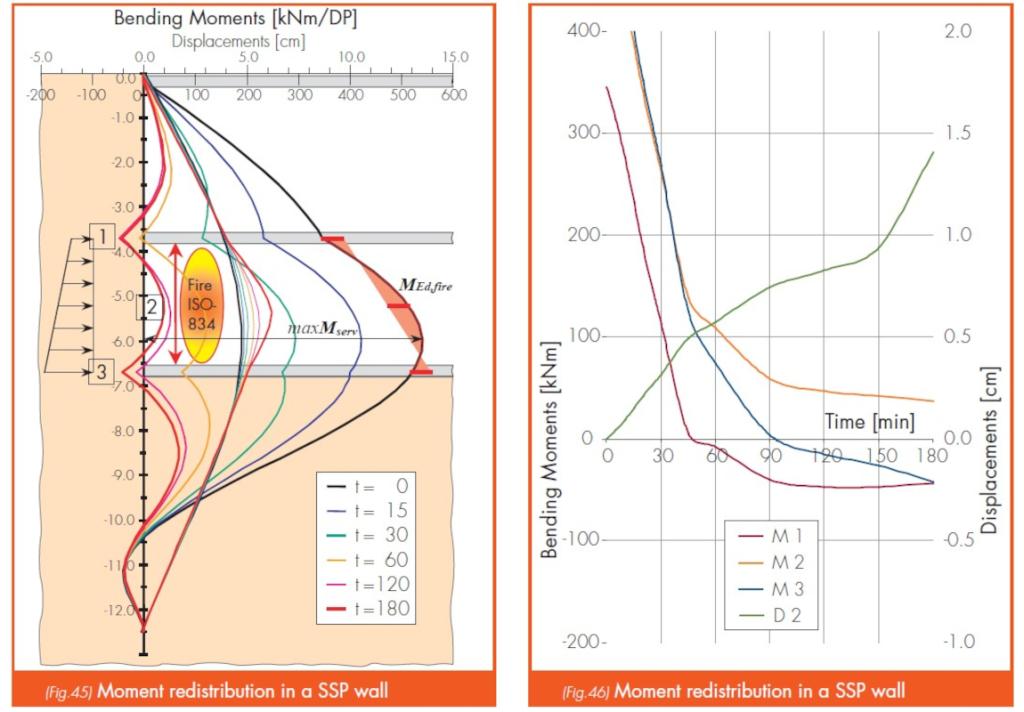
- Thermal properties of steel: steel’s strength decreases significantly at elevated temperatures. The mechanical properties can drop to about 10% of nominal values at 800°C. Structural analysis must therefore consider these changes to ensure adequate safety under fire conditions.
- Plastic redistribution of the bending moments: steel’s ability to redistribute stresses helps to maintain stability even when localized plastification occurs, which is particularly useful during fire events.
- Soil properties: impact on the calculations of the thermal conductivity of the soils and the water (acts as a sink, cooling effect).
- Passive protection of steel: as an option, concrete encasing or other measures can be considered in the software.
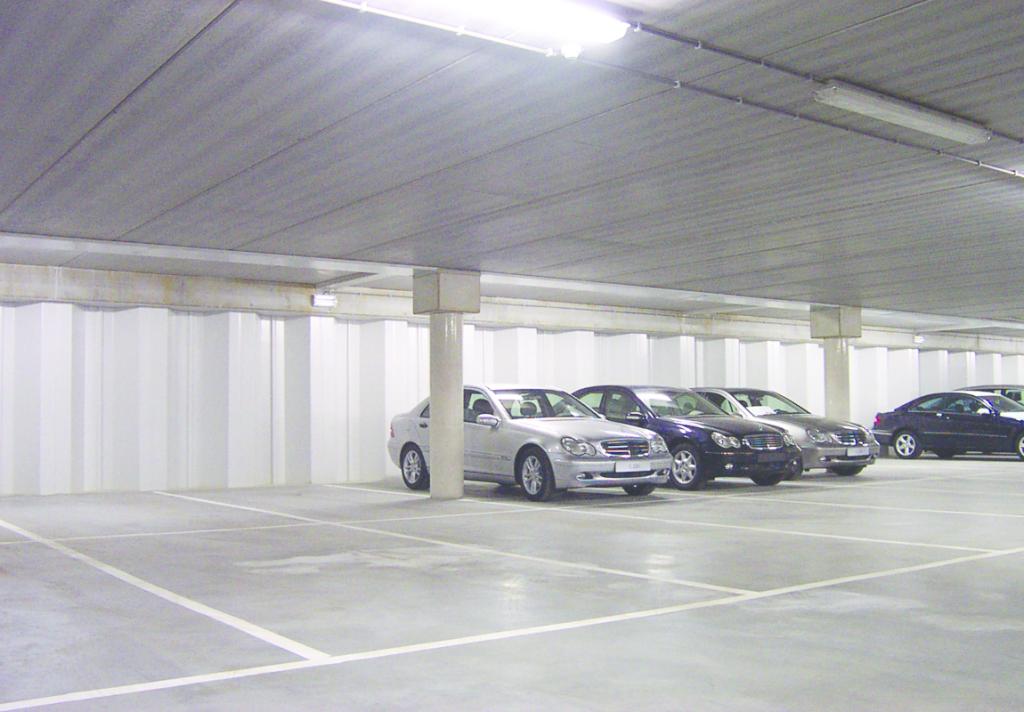

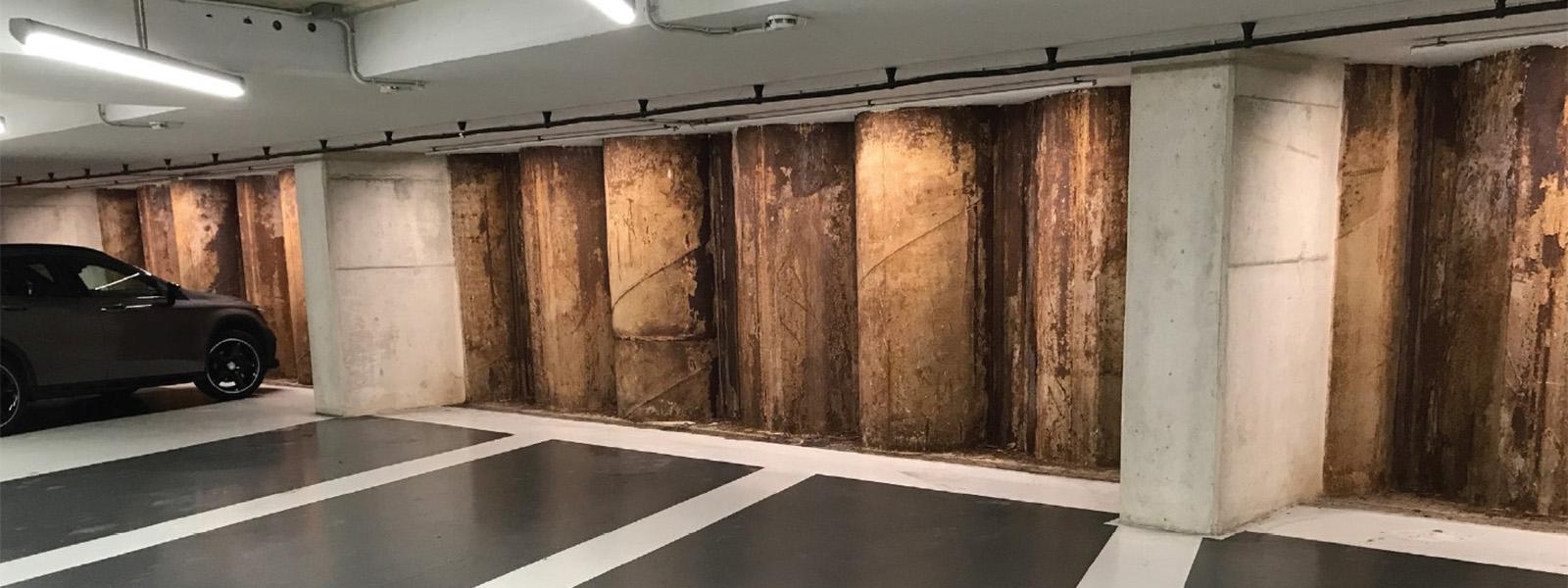
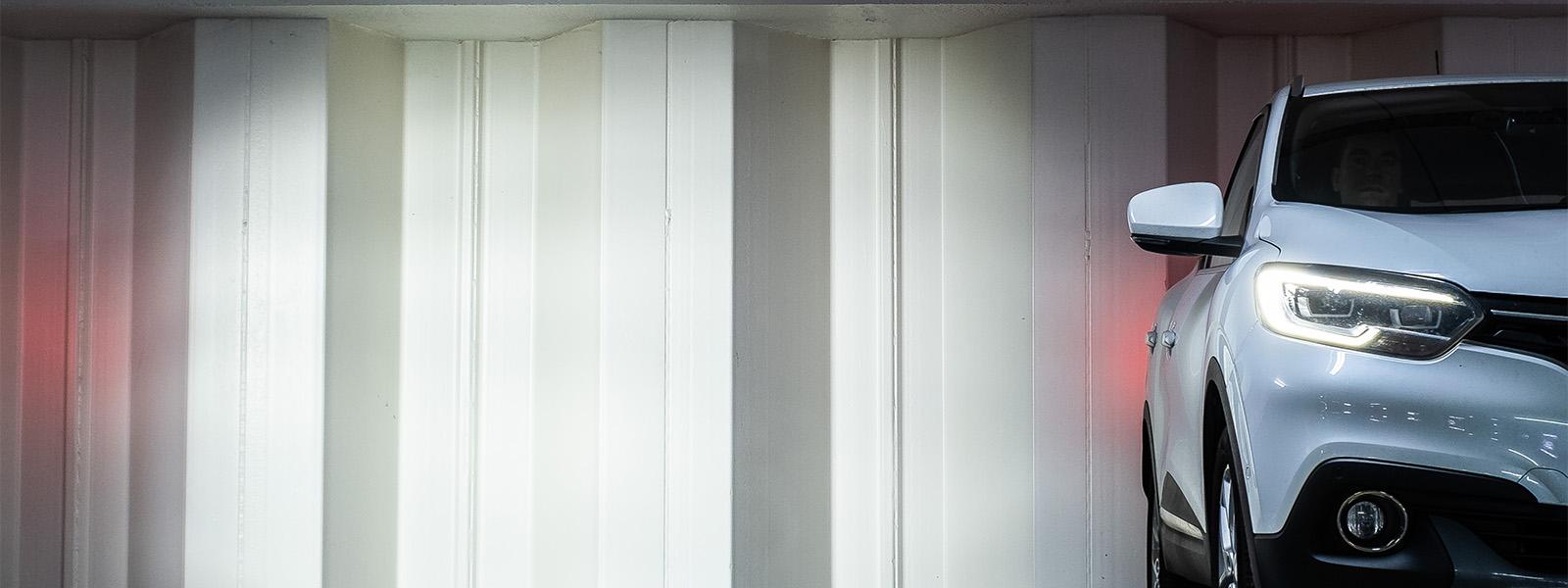
Mercedes-Benz Car Park, Ghent, Belgium: Steel sheet piles were used to provide a permanent structural solution. Fire resistance was enhanced using passive protection methods.
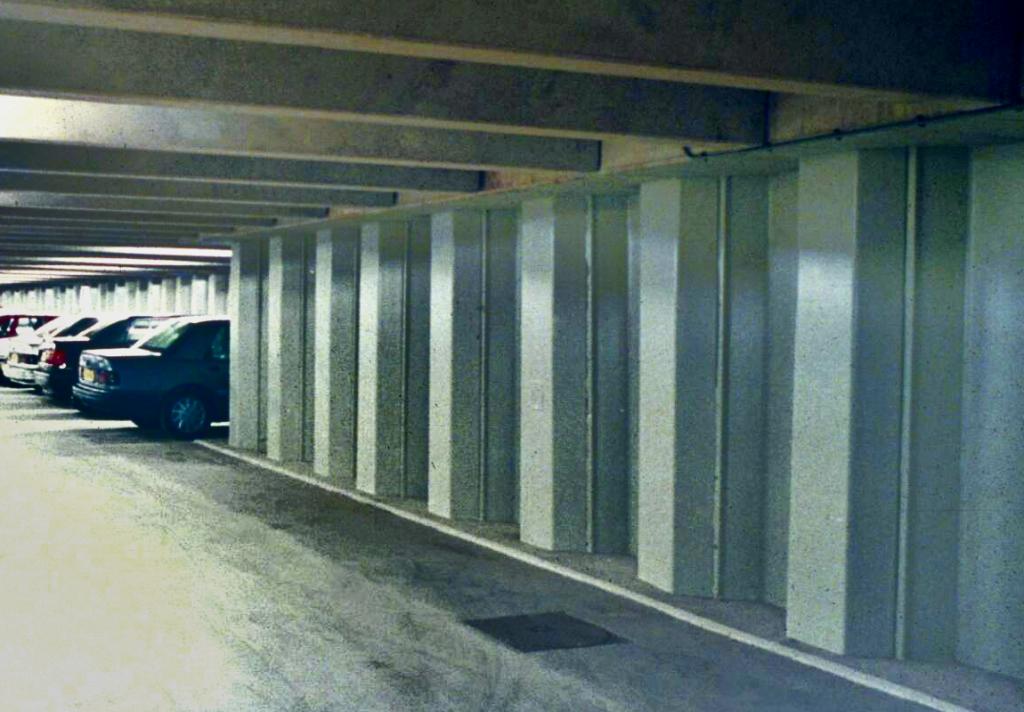

Car Park in The Hague, Netherlands: This underground parking structure showcases the adaptability of steel sheet piles in providing fire resistance and bearing significant loads.
Technical Support
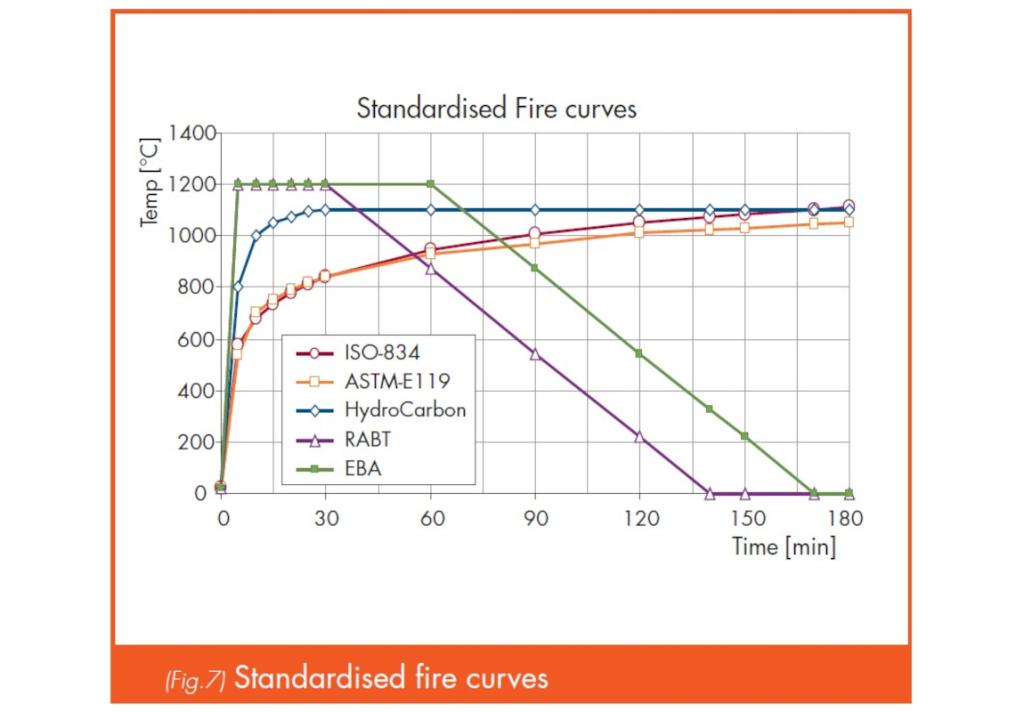
ArcelorMittal offers technical assistance in verifying the fire resistance of steel sheet pile structures, considering factors such as soil characteristics, load conditions, and fire scenarios (both standardized and natural).
With their ability to perform as both permanent retaining walls and structural bearing elements, steel sheet piles are a practical and cost-effective choice for underground construction and resilient against fire-related risks.