Reuse of Steel Sheet Piles - Best Practice
François Fohl and Oliver Hechler
Abstract
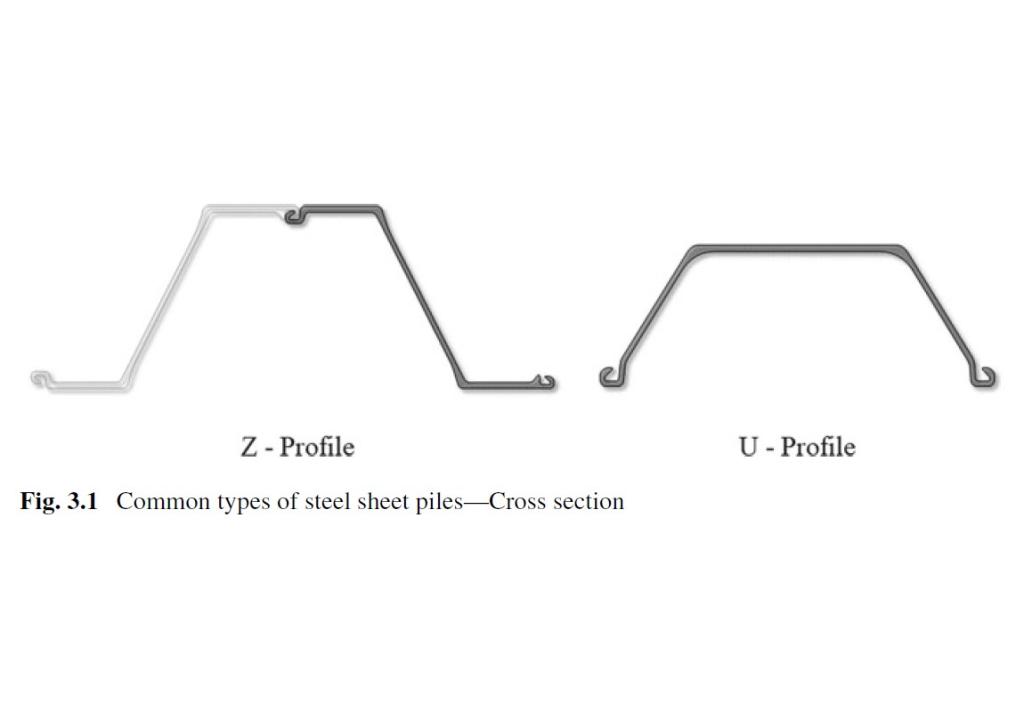
Steel sheet piles are used for retaining walls. Due to their modularity, they can be easily installed and extracted after their service life.
After their first use, they can be either directly recycled or reused several times and then recycled. The reuse of steel sheet piles allows to avoid new production and thus CO2-emissions for their production, reducing the environmental impacts per use.
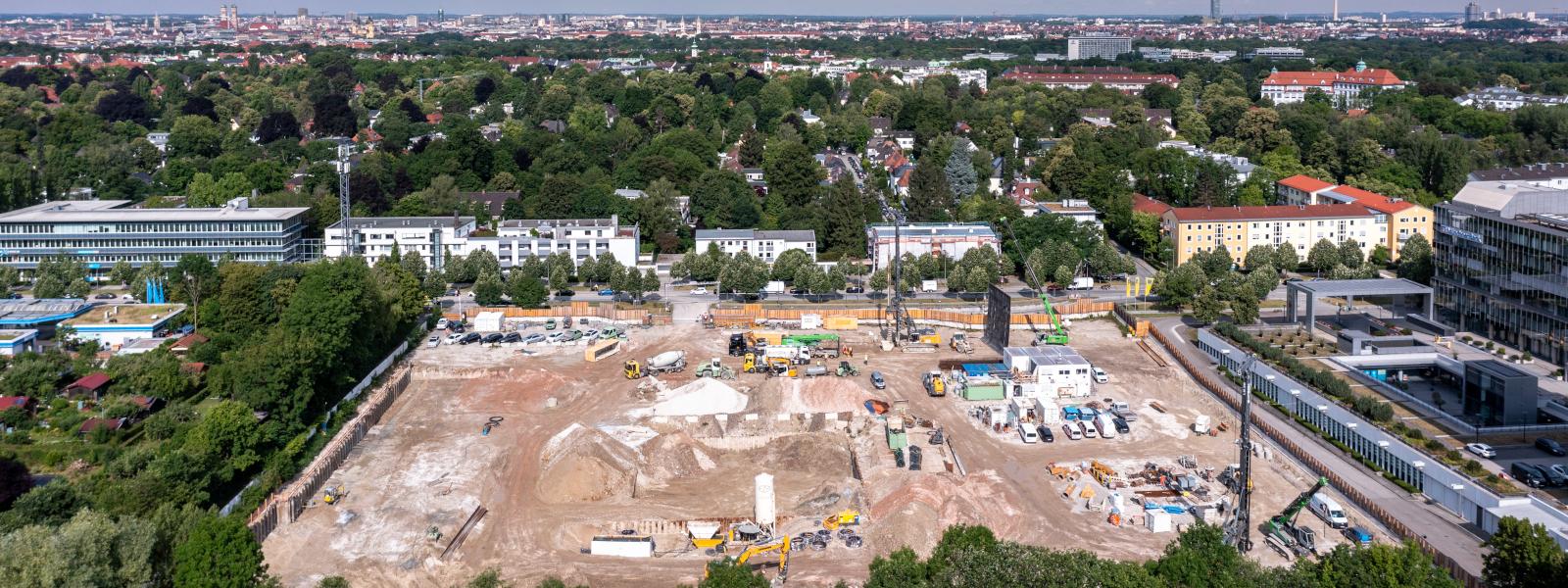
In temporary works, like construction pits, the reuse of sheet piles is common practice. Also, for certain permanent projects, there is no disadvantage in using second-hand sheet piles.
This article shows, on the basis of two case studies the best practice for reuse of sheet piles. The environmental impacts for a temporary project in Germany are discussed based on a Life Cycle Assessment for the sheet piling tonnage. Over the life cycle of the steel, 1 535 t of CO2-eq are emitted.
Reuse of the sections saved 79% of greenhouse gases. For a dyke reinforcement in the Netherlands, the project owner partly chose second-hand sheet piles to reduce the environmental impacts of the infrastructure project.
Keywords: Steel, Sheetpiles, Reuse, Environmentalimpacts
Download
 English
English
Circular Economy
Reduce Reuse Recycle