Half-time at the Saale-Elster viaduct, DE | 2006
The Milestone in Germany's Railway Infrastructure
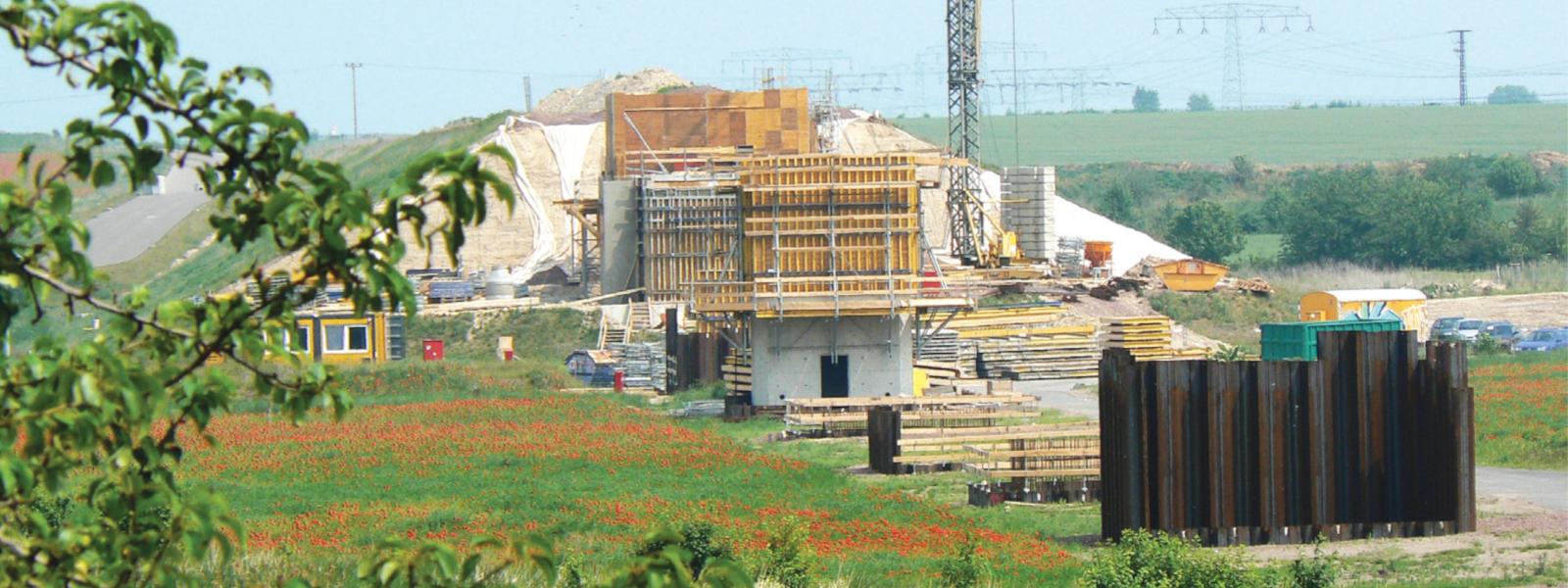
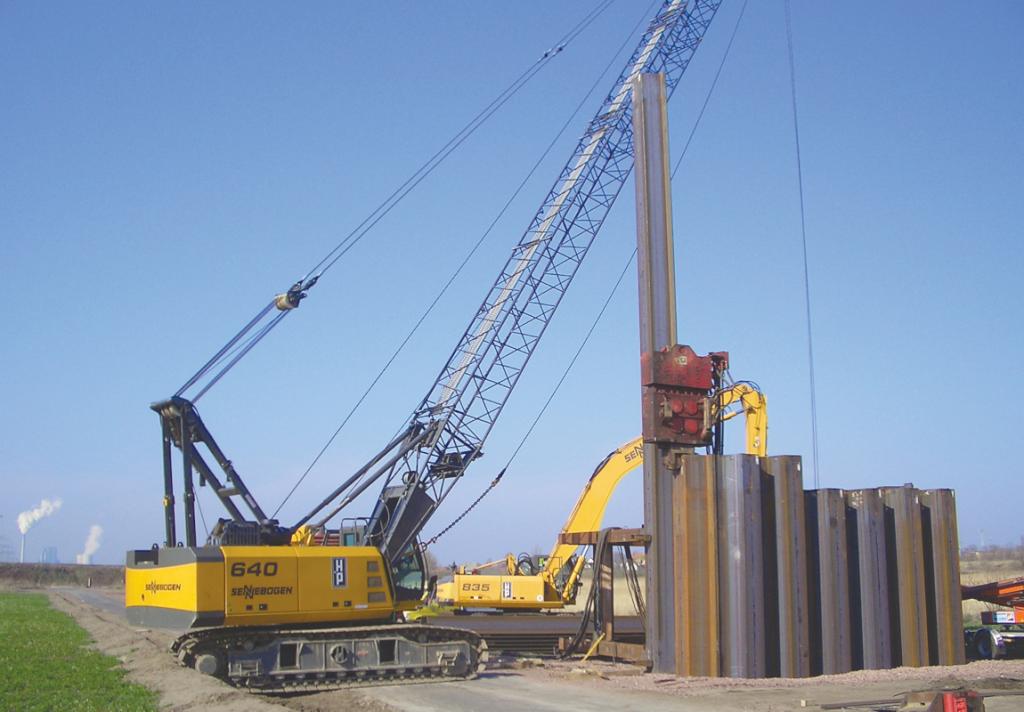
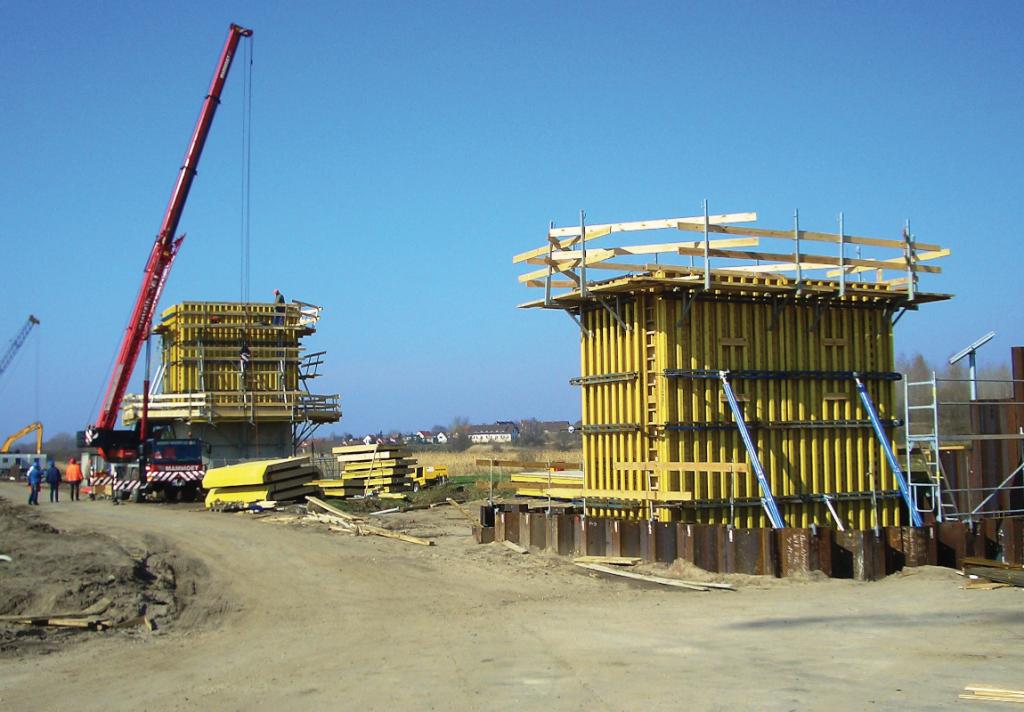
As part of the construction of the Erfurt-Leipzig/Halle railway line, the longest railway bridge in Germany was built from 2006 to 2012, located south of Halle.
Upon its completion, the bridge secured the transportation flows from Nuremberg to Berlin and from Frankfurt/M. to Dresden. The main bridge spans 6,456 meters across the Saale-Elster valley from east to west, with a branch towards Halle to the north spanning 2,112 meters at the center of the structure.
According to the plans of DB AG, the supporting structure is made of single-cell box girders made of prestressed concrete, and the superstructure system mainly consists of single-span girders with a 44-meter pillar distance.
Download
 German
German