Hazard Protection Solutions
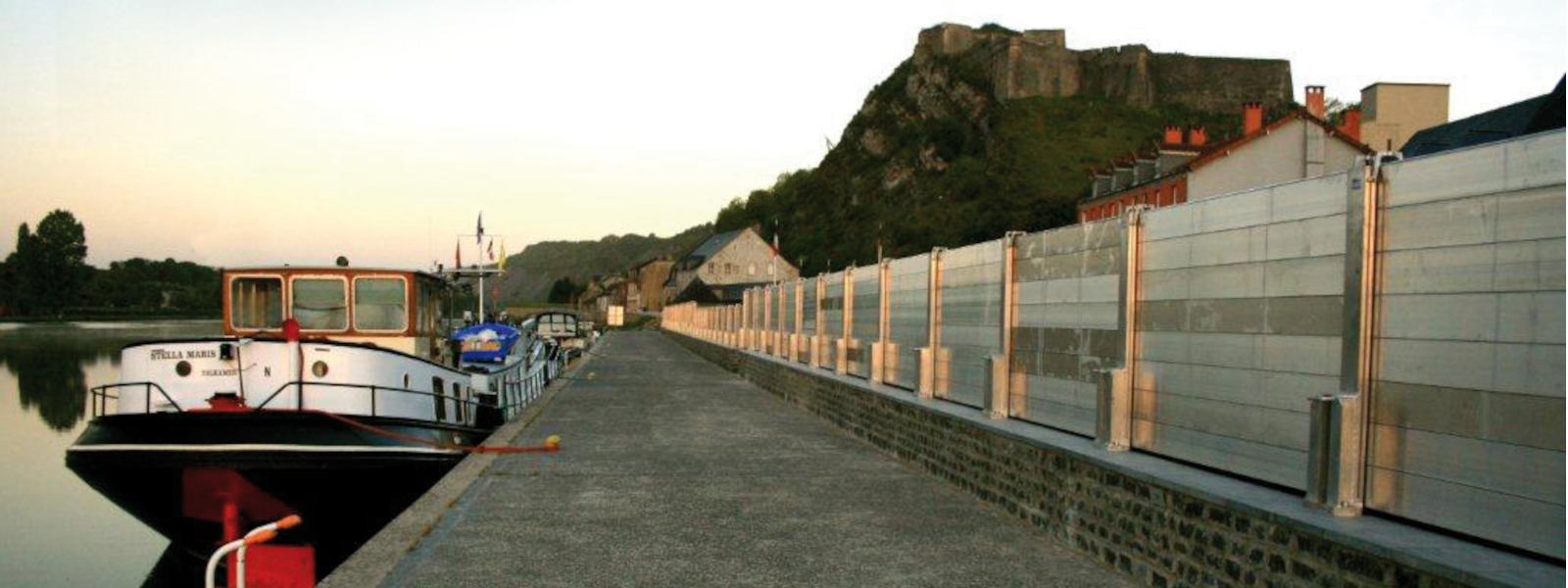
Flood defence, Givet, FR | 2010
Download the full case study
This 3 km-long project covering a footprint of more than 2900 m2 is the largest of its type ever carried out in France.
A special feature of this impressive project is that it involves demountable protection, as has been used by other towns in Europe (e.g. Bewdley in England and Cologne in Germany which holds the record for its 10 km along the Rhine). The Meuse is a plains river. Its flood rises slowly and gradually, generally after a long rainfall event, giving time to predict a flood and react by installing the defences as soon as the water is seen to start rising upstream. The installation time estimated by the Municipality of Givet is 48 hours (more than 650 posts to be bolted to baseplates and 3000 m2 of aluminium boards to be slotted into place).
The works were divided into a number of separate zones on the left and right banks of the Meuse. Three different types of flood defence are involved: fixed defences comprising walls of appropriate heights (0.9 to 3.2 m); demountable defences between 1.2 and 1.3 m high; and composite defences, comprising a wall combined with demountable defences, between 1.1 and 3.1 m high. The height of the fixed defences (walls) is based on the level of the twenty-year flood and that of the demountable defences on the level of the one-hundred-year flood. Sheet piles are used to create underground cutoffs. They prevent seepage below ground level and take the hydraulic thrust along a large part of the length on the right bank and in places on the left bank. They also serve as foundations for the defensive walls.
The soil investigations carried out generally showed that the top layer of loamy deposits is of poor quality. Deeper strata at between 4 and 7 m made up of sand and clayey, sandy gravel have quite good geotechnical properties. Below 7 m depth the subsoil is schist. The sheet piles were driven to depths of 4 to 5 m and as deep as 7 m in places, depending on the zone. They were driven with an ICE 625B vibratory unit powered directly by the hydraulic circuit of the excavator. In the Quai de Rancennes area an ICE 223 vibratory driver mounted on a KH150 (Hitachi) lattice-boom crane was used.
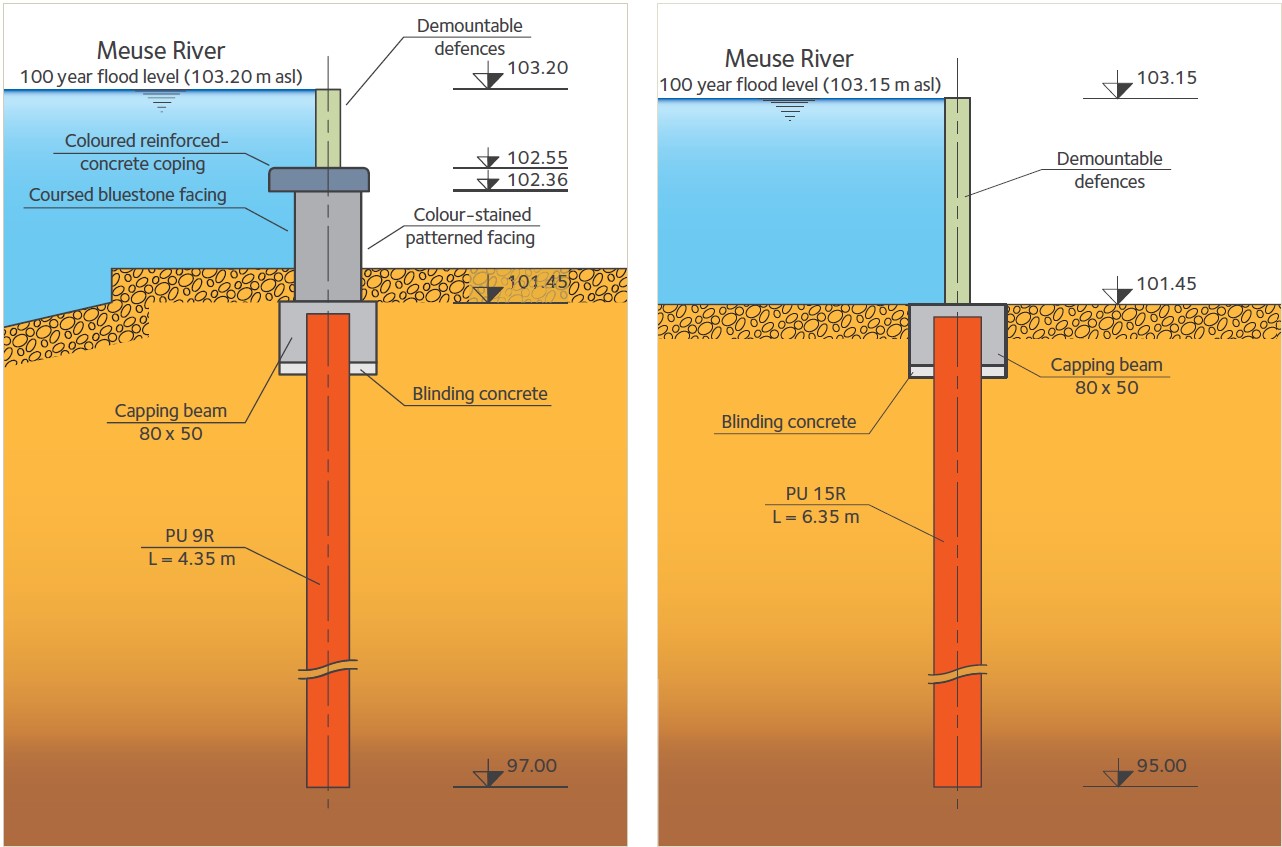
Reinforced-concrete coping beams were cast on top of the sheet pile walls and on top of these beams were built concrete walls with patterned colour-stained facings or Givet bluestone, depending on the zone. The baseplates and the slotted posts at the ends of sections of demountable defences were then fixed into the wall.
Behind the existing quaywall, a large concrete slabs was cast and serves as the foundation of the concrete wall.
A total of 850 tonnes of sheet piles, 750 baseplates, and 4000 m3 of Givet bluestone masonry were used.
The works were completed in mid 2011. On September 14, 2011, trial erection of the demountable defences was faster than expected (less than 48 hours). The real test will take place when the next 100-year flood occurs.
Givet is the northernmost point in the French part of the Meuse river valley, where a ‘finger’ of France reaches deep into the Belgian part of the Ardennes.
The town lies on both banks of the river, dominated by the Charlemont citadel atop a steep promontory upstream, on the left bank, and an old tower and ruined fortifications on Mont d’Haurs on the right bank.


