Water Transport Solutions
Maritime ports
10,334 tonnes of sheet piles
Dyke for a new polder, FR | 2021
Download the full case study
The marine works included the construction of a 400 m long quay wall with a draught of 12 m, platforms for the handling of heavy items (10 t/m2), and a dyke enclosing the 14 ha large polder. It also included dredging works in the commercial port, filling the polder with the dredged material and its consolidation to allow service surcharges suitable with the future industrial purposes. The construction of the quay wall (M01) and the dyke (M02) were part of the first stage of the project.
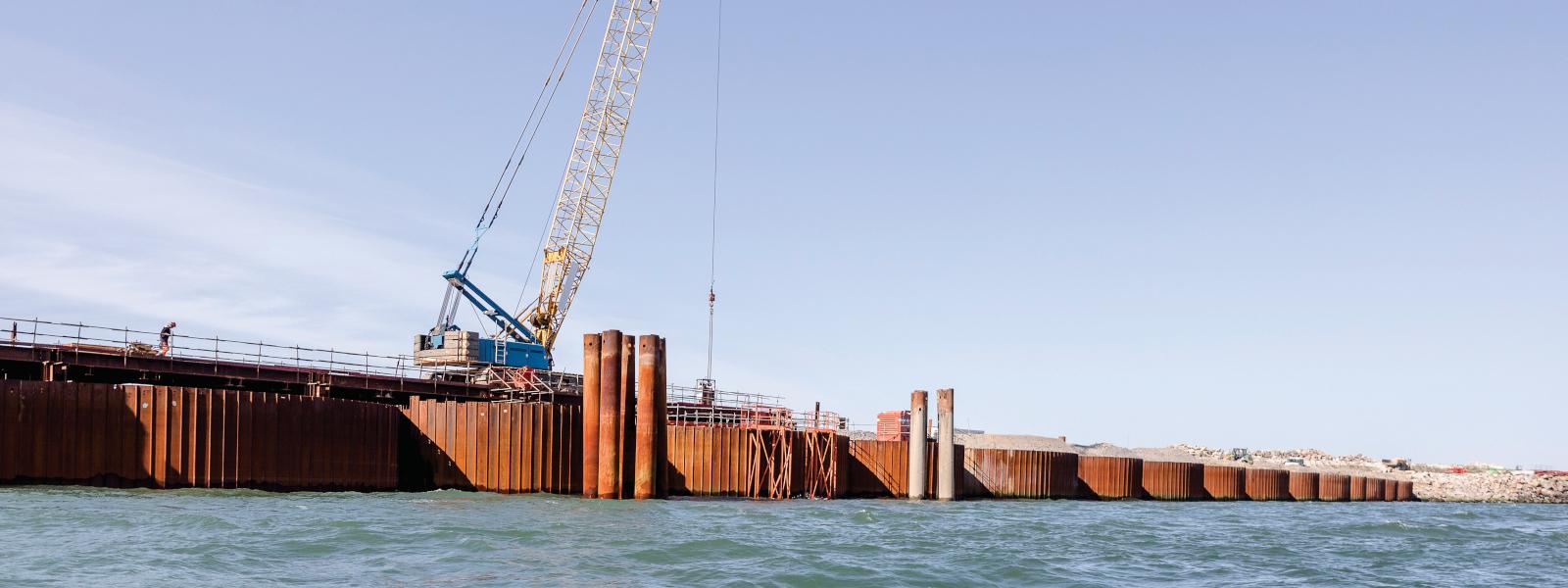
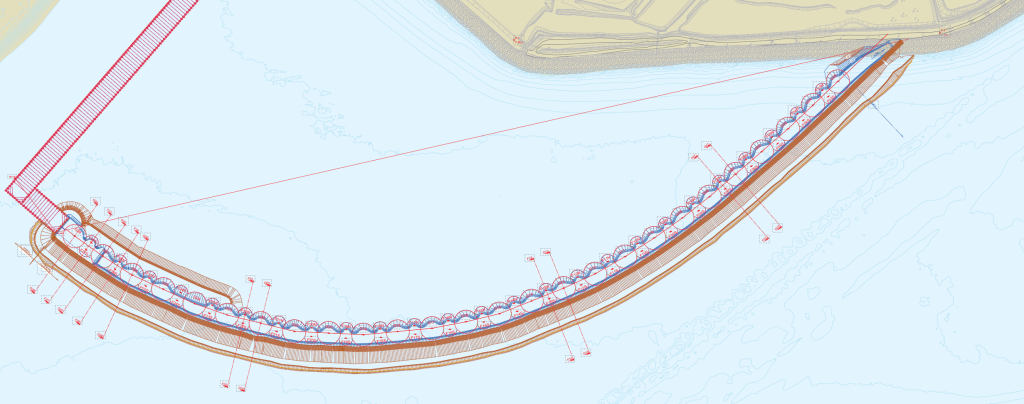
Lot M02 of the project consisted in the construction of a 860 m long dyke located between the existing polder shoreline and the M01 quay wall. The initial solution was an earth dyke built on top of a 105 m wide gravel substructure with a grain size from 10 to 80 mm. The core of the dyke was planned to be made of coarse fill material of a grain size of 30 to 500 mm. A filter layer of rock blocks of 60 to 300 kg and a cover made of hard rock blocks weighing between 1 and 3 tonnes completed the dyke design. The top level of the dyke is +13.50 m. For geotechnical stability reasons, the weak soil below the substructure had to be consolidated. Vertical drain columns were therefore installed down to the bedrock at a level varying between -23.00 and -12.00 m to accelerate this consolidation phase.
The construction company BOUYGUES Travaux Publics Régions France (BOUYGUES TPRF) was the leader of the tender-winning consortium consisting of Pigeon Bretagne Sud, Liziard, STPA and Sodraco. They suggested an alternative solution by replacing the standard earth core with a circular cells structure made of straight web steel sheet piles. This solution saved 500 000 m3 of fill material for the dyke and increased the landfill volume inside the polder by 120 000 m3.
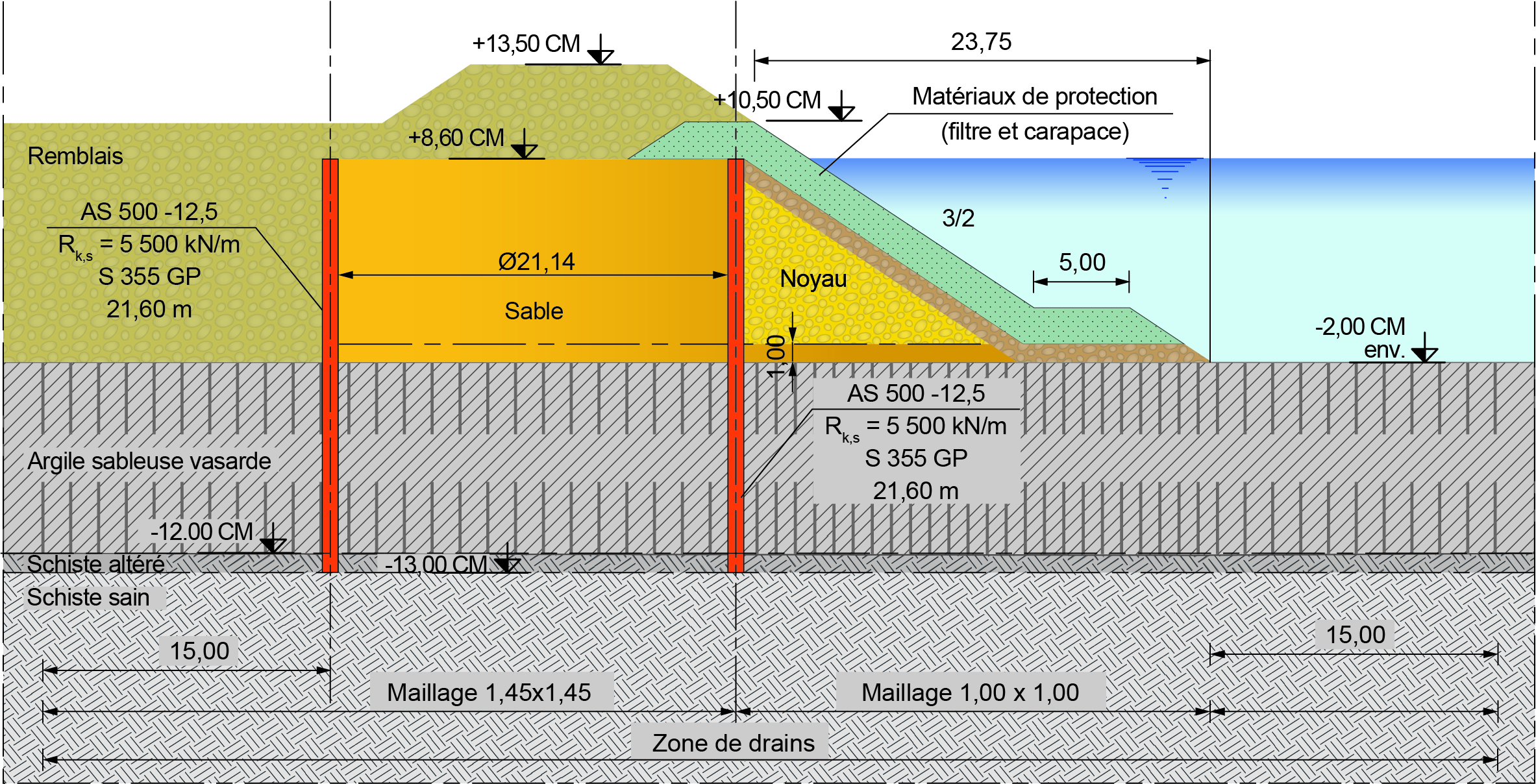
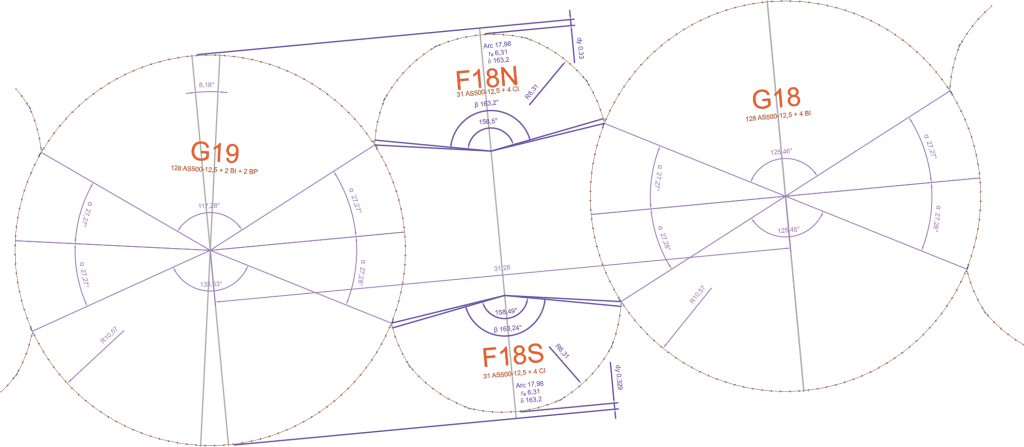
The design consultant SETEC International, assisted by TERRASOL geotechnical expert, was in charge of the design. The cells structure consists of 26 circular cells in 21.14 m diameter and of 50 intermediary arcs in 6.30 m radius. The cells and arcs are made of AS 500 straight web sheet piles with a web thickness of 12.50 mm. In S 355 GP steel grade, the sheet piles have an interlock resistance of 5 500 kN/m. The length of the sheet piles varied from 20.60 to 33.50 m to adapt to the variable level of the bedrock.
Due to the complex nature of the construction process of a cells structure, the Technical Department of BOUYGUES TP Régions France designed and built bespoke installation guides. These frames met the specific requirements of the project, in particular the diameter of the cells, and ensured the correct installation of the straight web sheet piles whilst also stabilizing the cell during assembly and backfill operations.
A floating pontoon was used to stock the equipment and materials and to carry the crane that installed the foundation piles for the temporary pier built inside the cells structure. The foundation piles also supported the installation frame.
The temporary pier then served as working platform for the installation of the straight web sheet piles and for the trucks and excavators in charge of the filling works.
The sheet piles were installed with a PTC 24HFV vibrodriver (with high frequency and variable moment), attached to the boom of a Hitachi Sumitomo SCX-2800 crawler crane. Acting with a centrifugal force of 1 419 kN, this vibrodriver was well suited to drive the straight web sheet piles, even the 33.5 m long ones, down to the bedrock at -23.00 m.