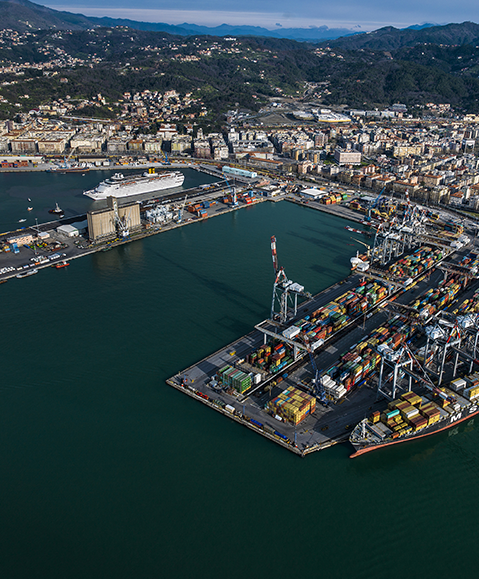
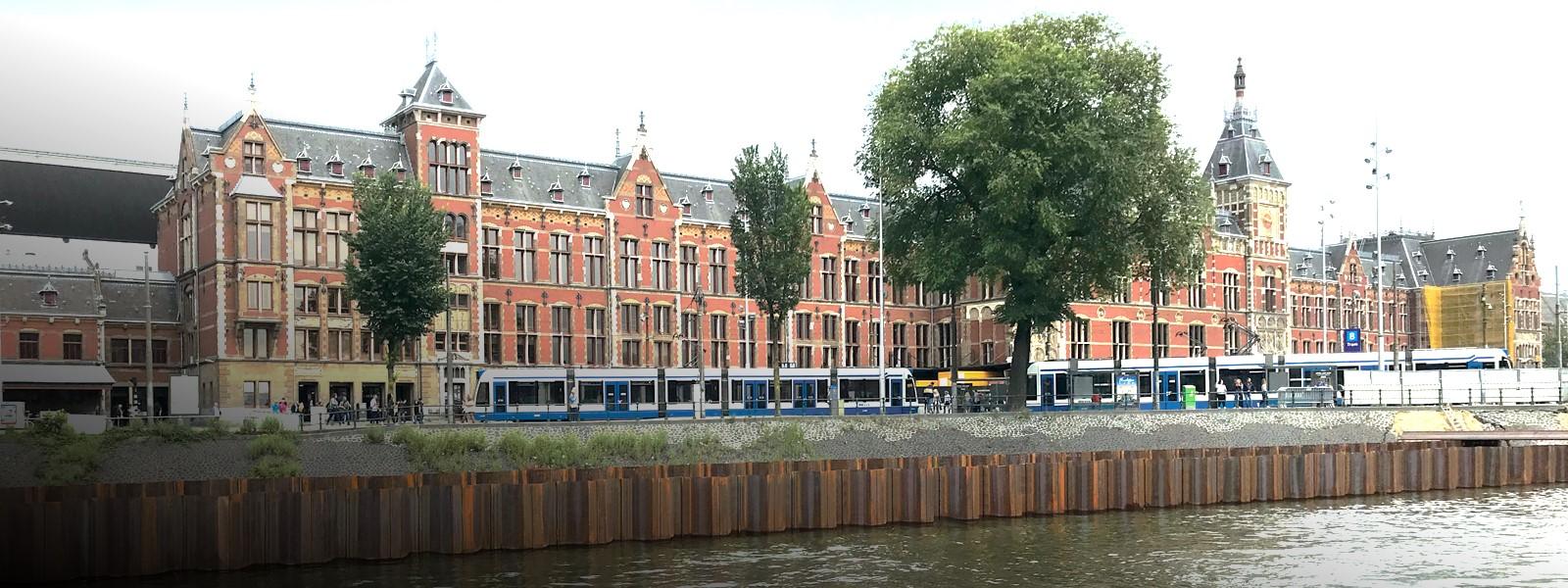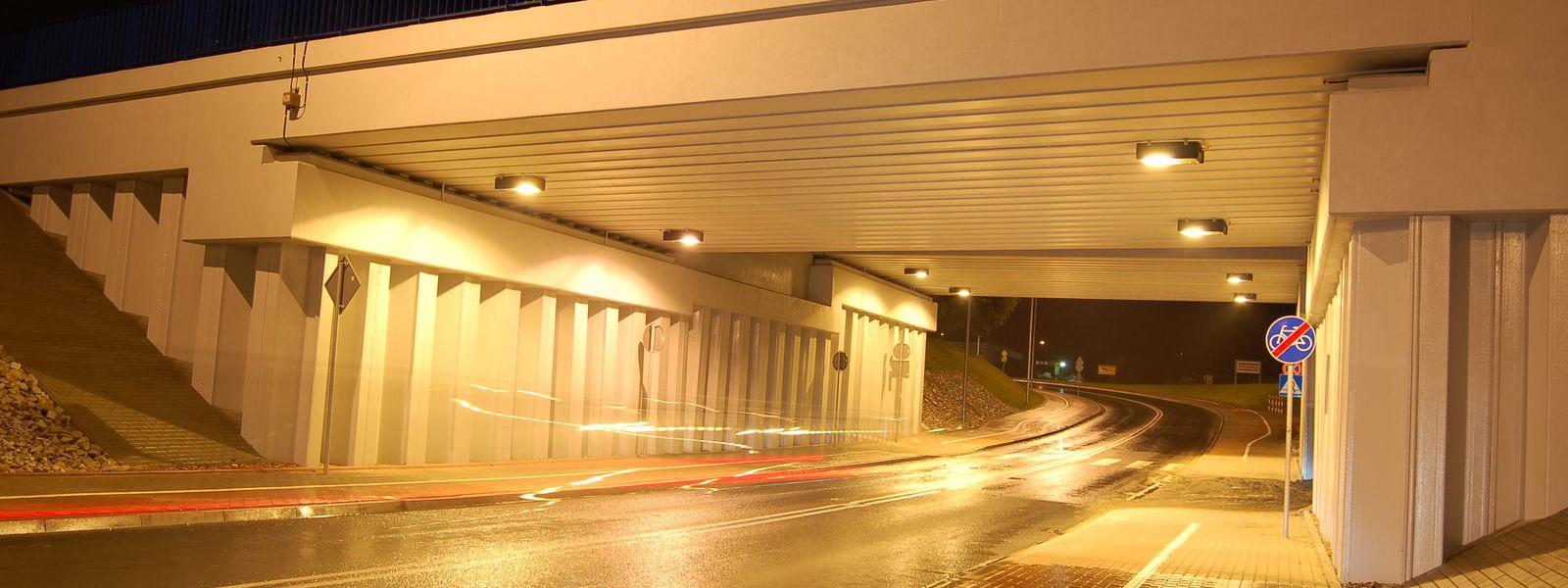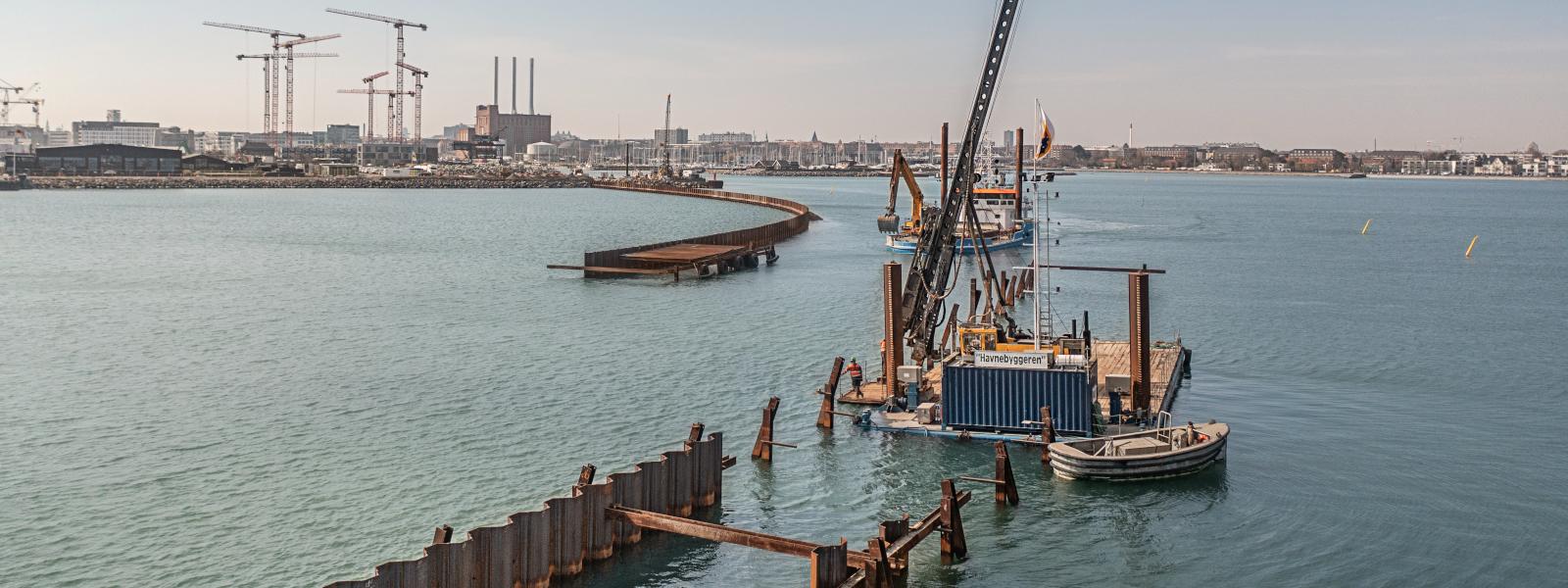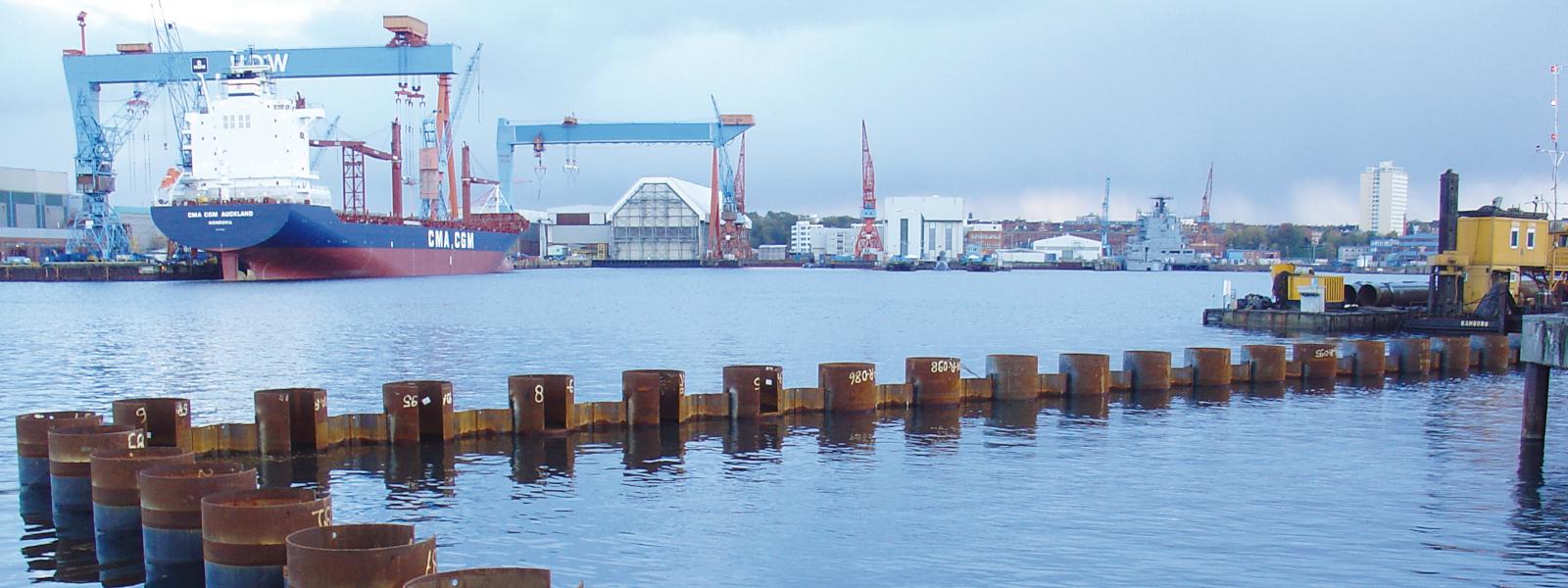
Water Transport Solutions
ArcelorMittal’s hot rolled steel sheet pile sections have been used to build maritime infrastructures for over a hundred years.
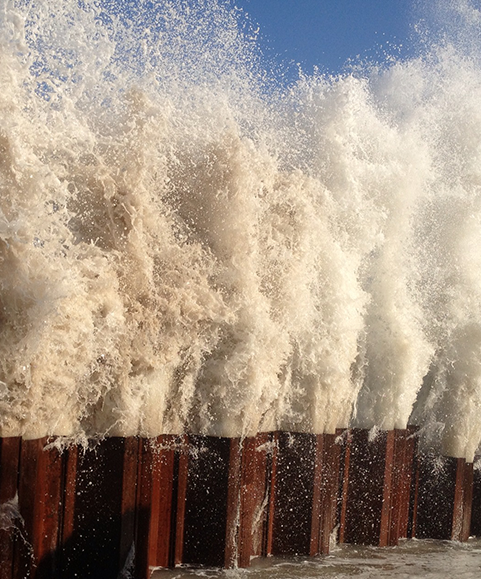


Hazard Protection Solutions
Flood defences and coastal erosion barriers made with sheet piles help safeguard our communities from natural disasters.
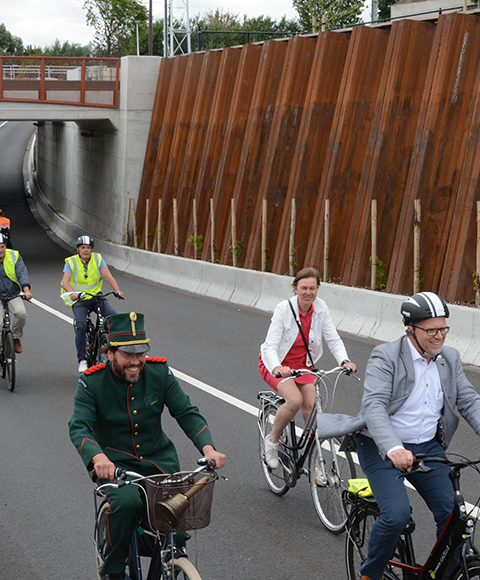


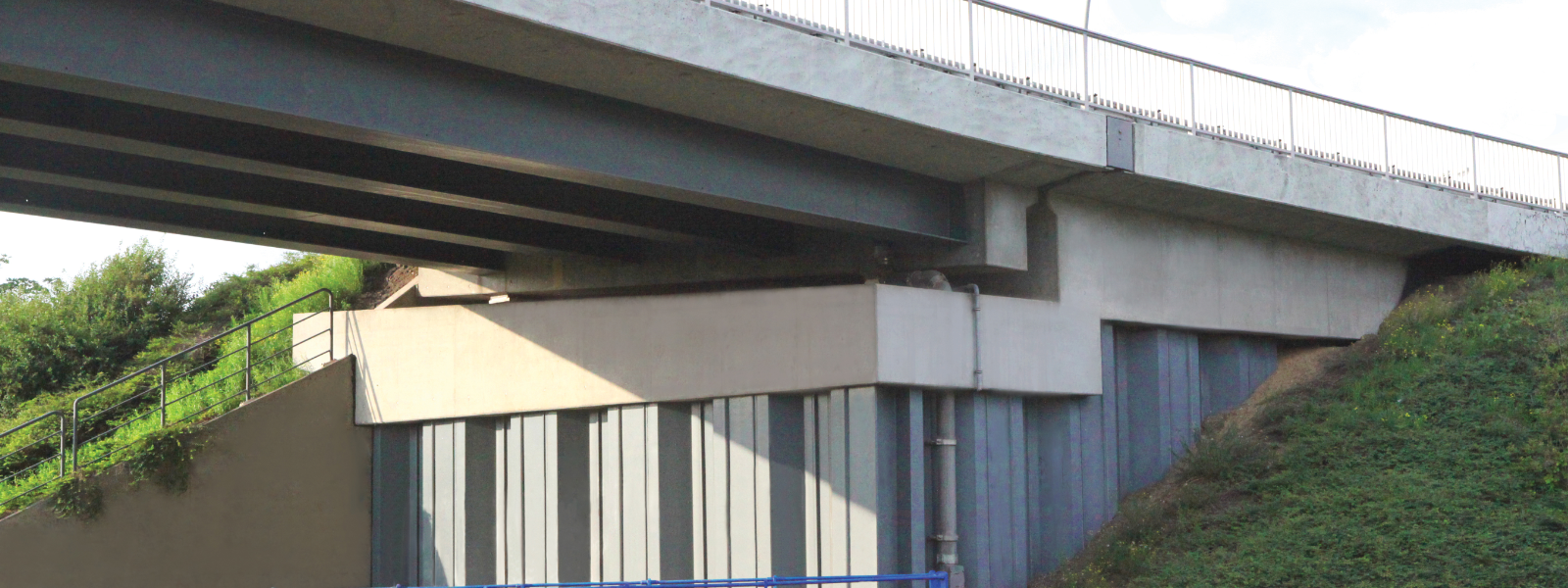
Mobility Infrastructure Solutions
Steel sheet piles are commonly used to build road and railway infrastructures.


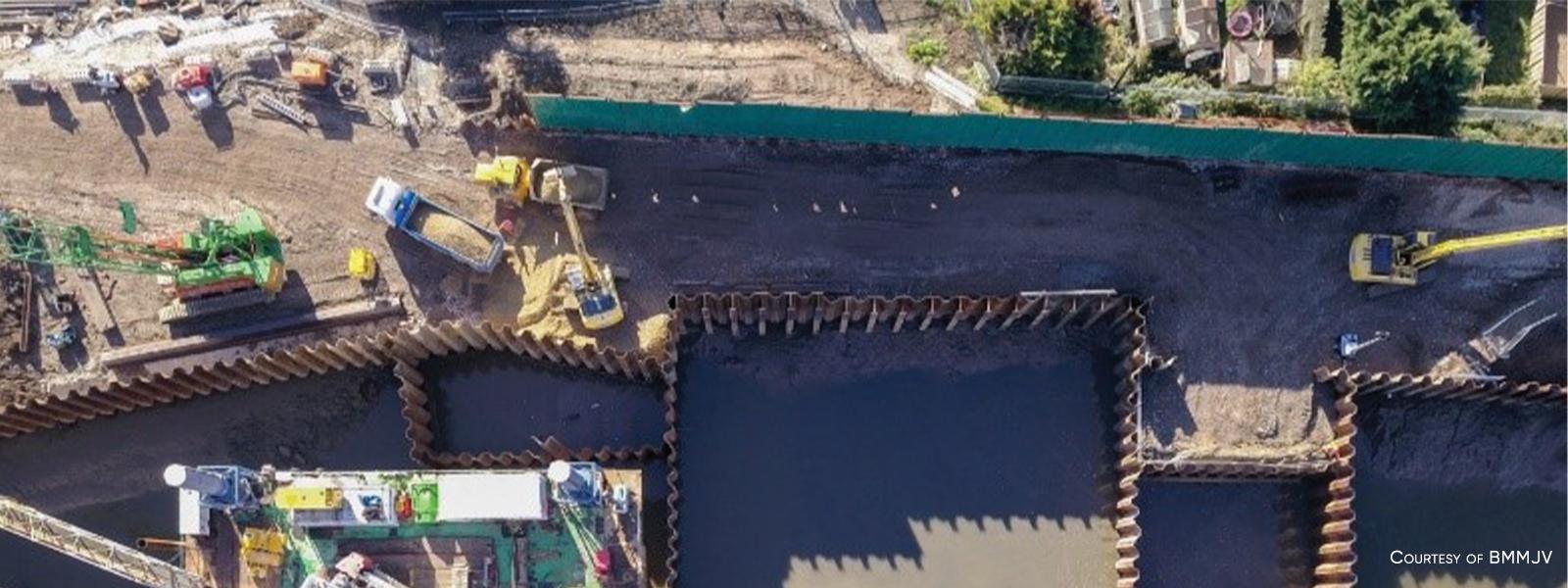
Environmental Protection Solutions
Steel sheet piles are used as temporary and permanent retaining walls for landfill conversion, polluted soil remediation, riverbed cleaning operations and pollution containment.
How can steel sheet piles help you?
Find out arguments and technical information to help you select the right solutions

Products and services
Production range, steel grades, services (rental, special piles,...), free support (design, recommendations), and more ...

Specific technical aspects
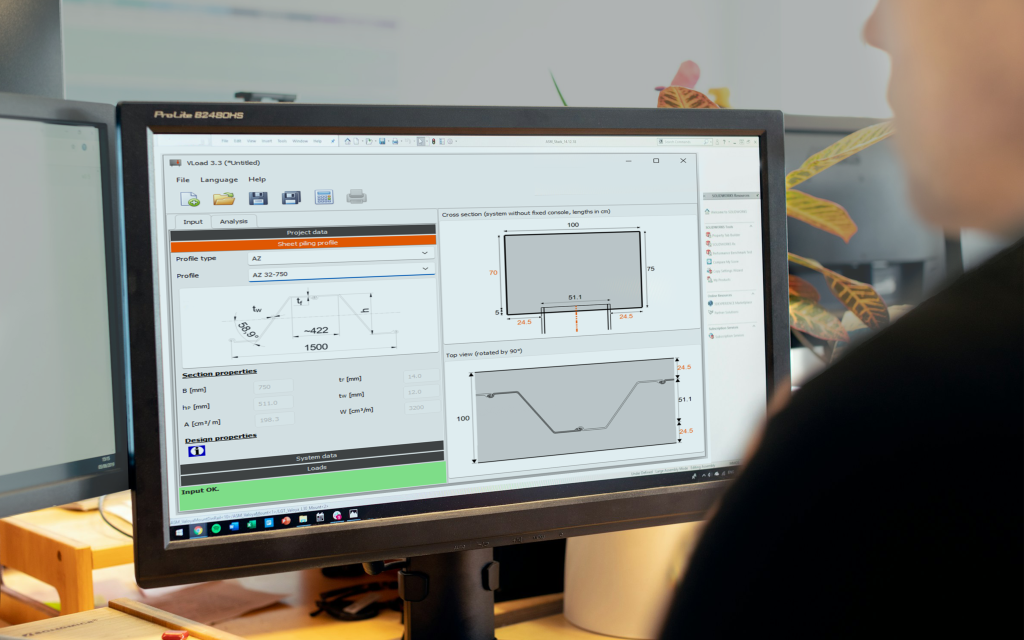
Learn more about the benefits and technical aspects of sheet piling, from the design of sustainable and resilient sheet pile walls, to digitalization and installation.

Sustainable steel foundation solutions
Learn more about steel sheet piling and the circular economy: Reduce – Reuse – Recycle